Discrete Manufacturing: What It Is and How It Powers India’s Industrial Growth
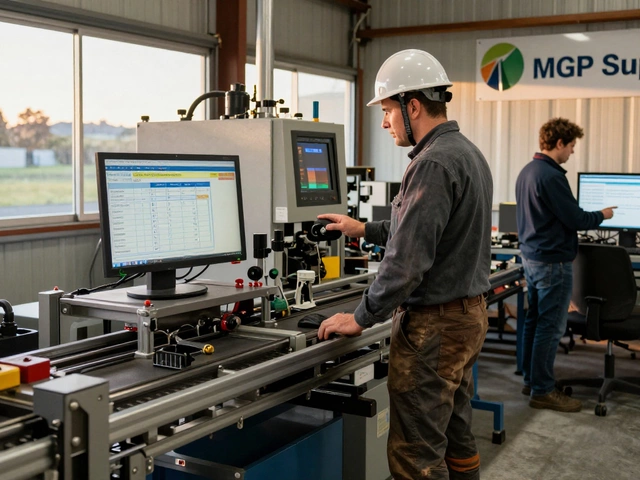
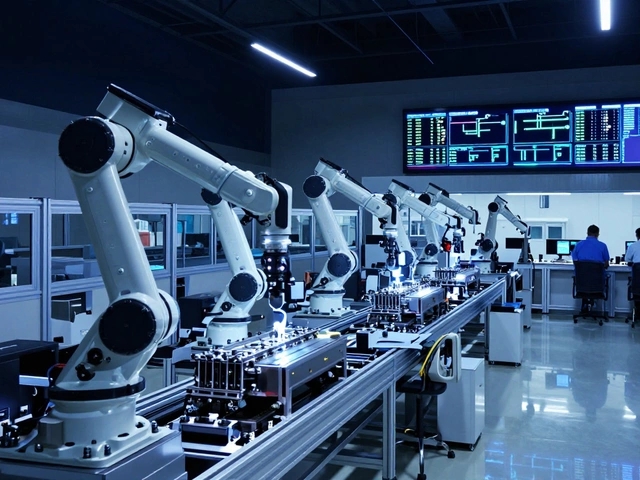
When you think of manufacturing, you might picture a factory churning out identical products on a never-ending line. But discrete manufacturing, a type of production where individual units are made separately, often with custom steps. Also known as job shop manufacturing, it’s how India builds smartphones, medical devices, solar inverters, and even custom machinery—one unit at a time. Unlike process manufacturing (which mixes ingredients like chemicals or food), discrete manufacturing deals with parts that can be taken apart, counted, and tracked. Each product has a unique bill of materials, assembly sequence, and quality check. It’s not just about volume—it’s about control, precision, and adaptability.
This approach powers small and medium factories across Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Maharashtra, where makers build batches of 50 or 5,000 units based on real orders. You’ll find it in electronics assembly lines where workers install motherboards, in plastic component shops where injection molds create custom housings, and in medical device makers who assemble ventilator parts with strict traceability. Small manufacturers, businesses that produce goods in limited quantities with hands-on oversight. Also known as local makers, they thrive under discrete manufacturing because it lets them pivot fast, test designs, and serve niche markets without huge upfront costs. This is why you see startups in Bengaluru pitching prototypes to local shops that can turn an idea into 100 working units in two weeks. It’s also why government schemes like Make in India focus on boosting this sector—because it creates skilled jobs, reduces import reliance, and scales smarter than mass production ever could.
What makes discrete manufacturing different?
It’s not just about the product—it’s about the process. In discrete manufacturing, you track each unit with serial numbers. You stop the line if one part fails. You rework a single unit instead of scrapping a whole batch. That’s why tools like the 5 M’s of manufacturing, Manpower, Machines, Materials, Methods, and Measurement. Also known as manufacturing principles are so critical here. They help small factories stay lean, avoid waste, and qualify for subsidies. Compare that to process manufacturing, where you can’t unmix a chemical blend. Discrete manufacturing gives you room to fix mistakes, upgrade designs, and respond to customer feedback—fast.
India’s rise in electronics exports isn’t just because of big brands. It’s because hundreds of small shops across the country can build, test, and ship discrete products—like circuit boards, chargers, and sensors—with quality that meets global standards. You’ll find these same shops in the posts below, showing how startups secure funding, pitch ideas, and nail profit margins by mastering this exact model. Whether you’re a founder, investor, or just curious, what follows is a real-world look at how discrete manufacturing is changing India’s industrial future—one product at a time.