Processing Units: Types, Uses, and How They Power Indian Manufacturing
When you think of processing units, systems that transform raw materials into finished goods through controlled steps. Also known as production lines, they are the hidden engines behind everything from packaged snacks to smartphone parts made in India. These aren’t just machines—they’re organized systems that decide how fast, how clean, and how cheaply a product gets made.
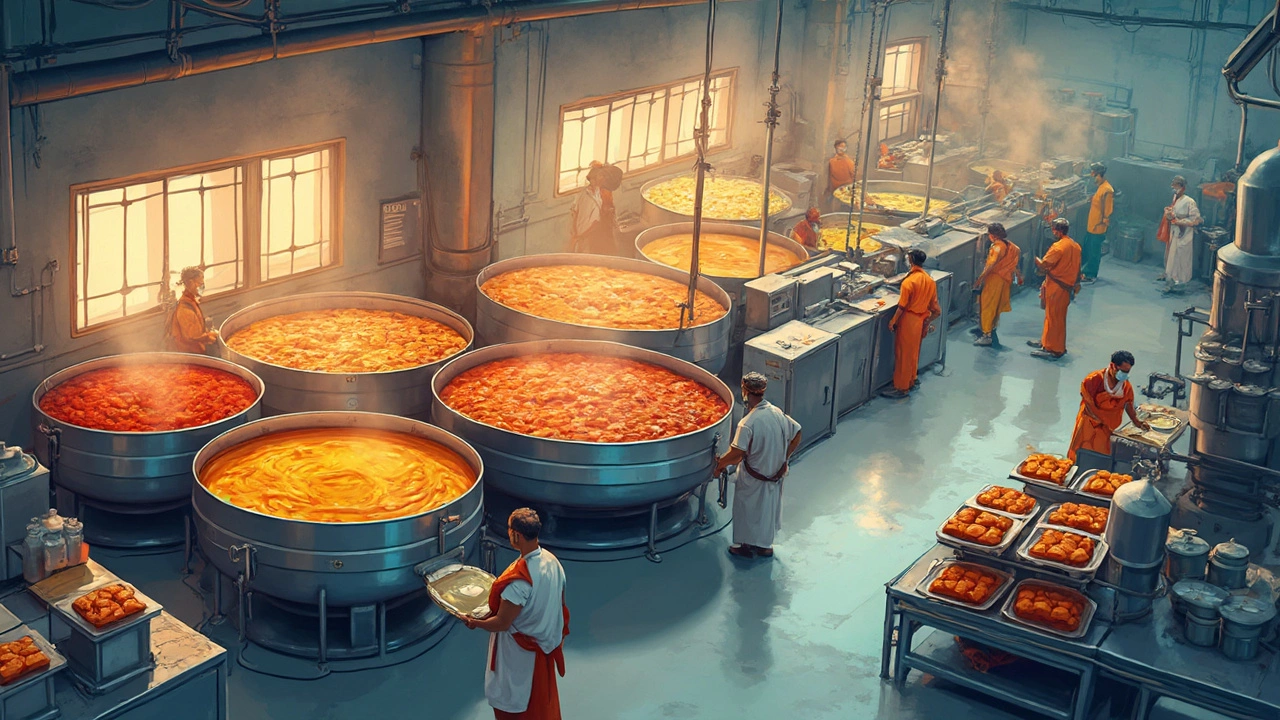
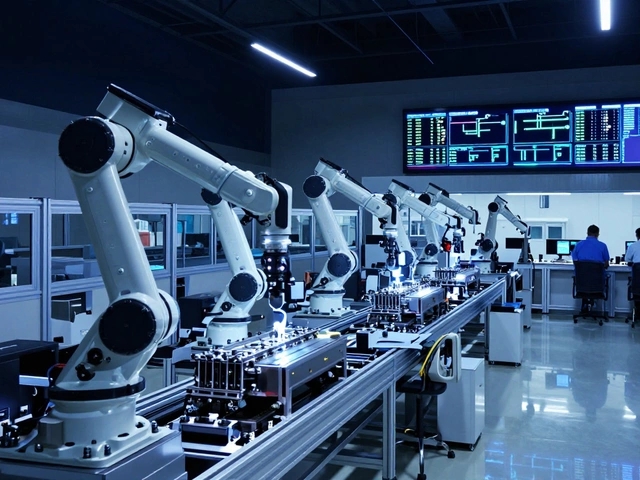
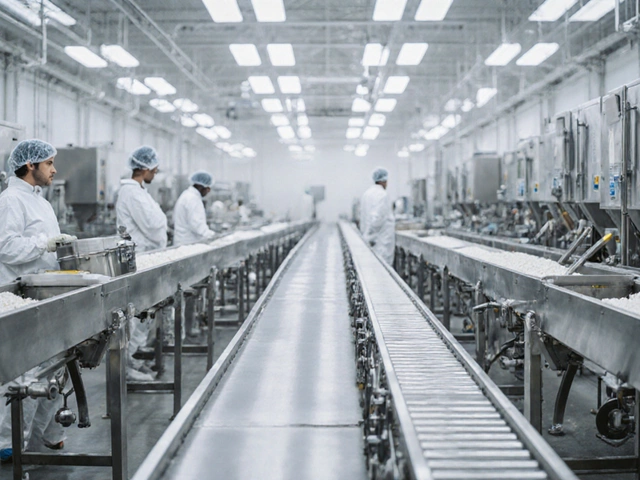
There are different kinds of processing units, structured workflows designed for specific types of production, and picking the wrong one can cost you time, money, and customers. Batch processing, making products in small groups, one step at a time works great for custom or low-volume items like specialty snacks or medical devices. Continuous processing, running non-stop with materials flowing through a line is what big factories use for things like sugar, plastic pellets, or solar inverters—where volume matters more than customization. Then there’s hybrid processing, a mix of both, letting you scale without overhauling your whole setup. The right choice depends on your product, your budget, and how fast you want to grow.
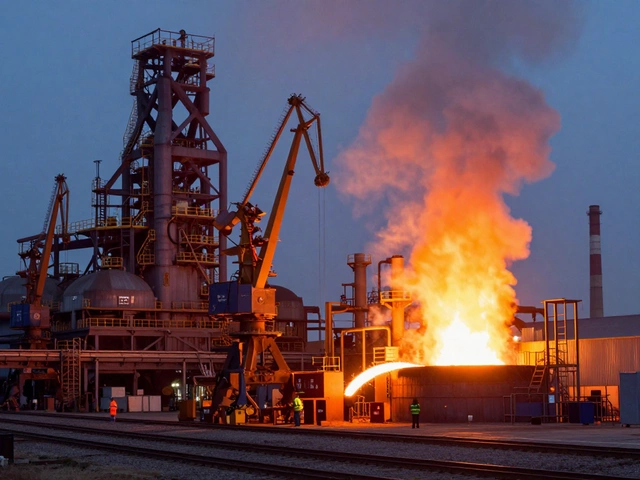
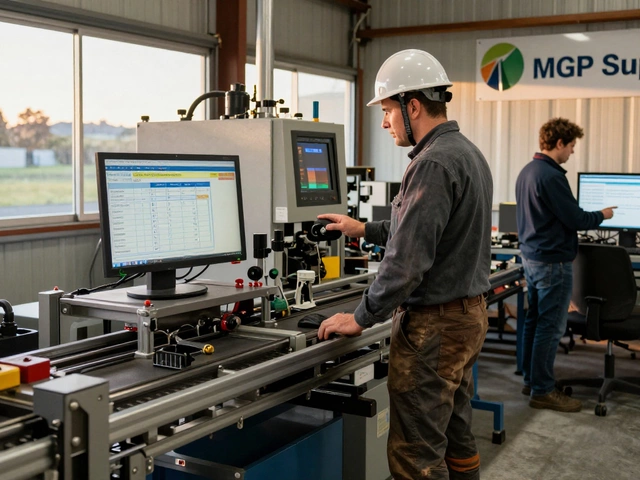
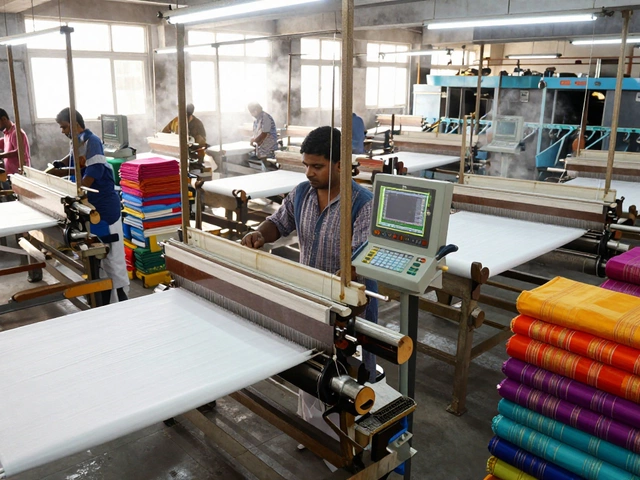
Indian manufacturers are shifting fast. Smaller factories that once relied on hand tools now use automated processing units to meet export standards. Food processors in Tamil Nadu, plastic makers in Gujarat, and electronics assemblers in Karnataka all depend on these systems—not just to make things, but to prove they can make them consistently. Government schemes even reward factories that upgrade to efficient processing units with subsidies and training. That’s why knowing the difference between a batch line and a continuous line isn’t just technical—it’s a business move.
What you’ll find below are real examples of how processing units work in India—what’s being made, who’s making it, and which type of unit gives the best return. No theory. No fluff. Just what’s happening in factories right now.